Just a half-century ago, very little was known about the genetic factors that contribute to human disease . The Human Genome Project (HGP) was one of the great feats of exploration
in history - an inward voyage of discovery rather than an outward
exploration of the planet or the cosmos; an international research
effort to sequence and map all of the genes - together known as the
genome - of members of our species, Homo sapiens. In 1990, researchers from around the world launched the Human Genome Project. Their goal: to determine the sequence of the 3 billion building blocks, or letters, in our DNA instruction manual. Led in the United States by the National Human Genome Research Institute and the Department of Energy, the Human Genome Project was completed in April 2003. The HGP gave us the ability, for the first time, to read
nature's complete genetic blueprint for building a human being.

Why Human Genome ? Hidden among these billions of letters is information that will expand our knowledge of human body and improve human health. The
Human Genome Project’s goal was to provide researchers with powerful
tools to understand the genetic factors in human disease, paving the way
for new strategies for their diagnosis, treatment and prevention. From the start, the Human Genome Project
supported an Ethical, Legal and Social Implications research program to
address the many complex issues that might arise from this science. All data generated by the Human Genome Project
were made freely and rapidly available on the Internet, serving to
accelerate the pace of medical discovery around the globe. The Human Genome project spurred a revolution in biotechnology innovation around the world.
The current progress on Human Genome project
- The Human Genome Project has already fueled the discovery of more than 1,800 disease genes.
- As a result of the Human Genome Project,
today’s researchers can find a gene suspected of causing an inherited
disease in a matter of days, rather than the years it took before the
genome sequence was in hand.
- There are now more than 2,000 genetic tests for
human conditions. These tests enable patients to learn their genetic
risks for disease and also help healthcare professionals to diagnose
disease.
- At least 350 biotechnology-based products resulting from the Human Genome Project are currently in clinical trials.
- Having the complete sequence of the human
genome is similar to having all the pages of a manual needed to make the
human body. The challenge now is to determine how to read the contents
of these pages and understand how all of these many, complex parts work
together in human health and disease.
- One major step toward such comprehensive understanding was the development in 2005 of the HapMap (http://hapmap.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/),
which is a catalog of common genetic variation, or haplotypes, in the
human genome. In 2010, the third phase of the HapMap project was
published, with data from 11 global populations, the largest survey of
human genetic variation performed to date. HapMap data have accelerated
the search for genes involved in common human diseases, and have already
yielded impressive results in finding genetic factors involved in
conditions ranging from age-related blindness to obesity.
- The tools created through the Human Genome
Project continue to underlie efforts to characterize the genomes of
important organisms used extensively in biomedical research, including
fruit flies, roundworms, and mice.
- NIH’s Ethical, Legal and Social Implications
program has become a model for other research efforts seeking to address
ethical issues in a proactive manner (http://www.genome.gov/10001618).
- With the drastic decline in the cost of
sequencing whole exomes or genomes, groundbreaking comparative genomic
studies are now identifiying the causes of rare diseases such as Kabuki
and Miller syndromes.
- Much work still remains to be done. Despite
many important genetic discoveries, the genetics of complex diseases
such as heart disease are still far from clear.

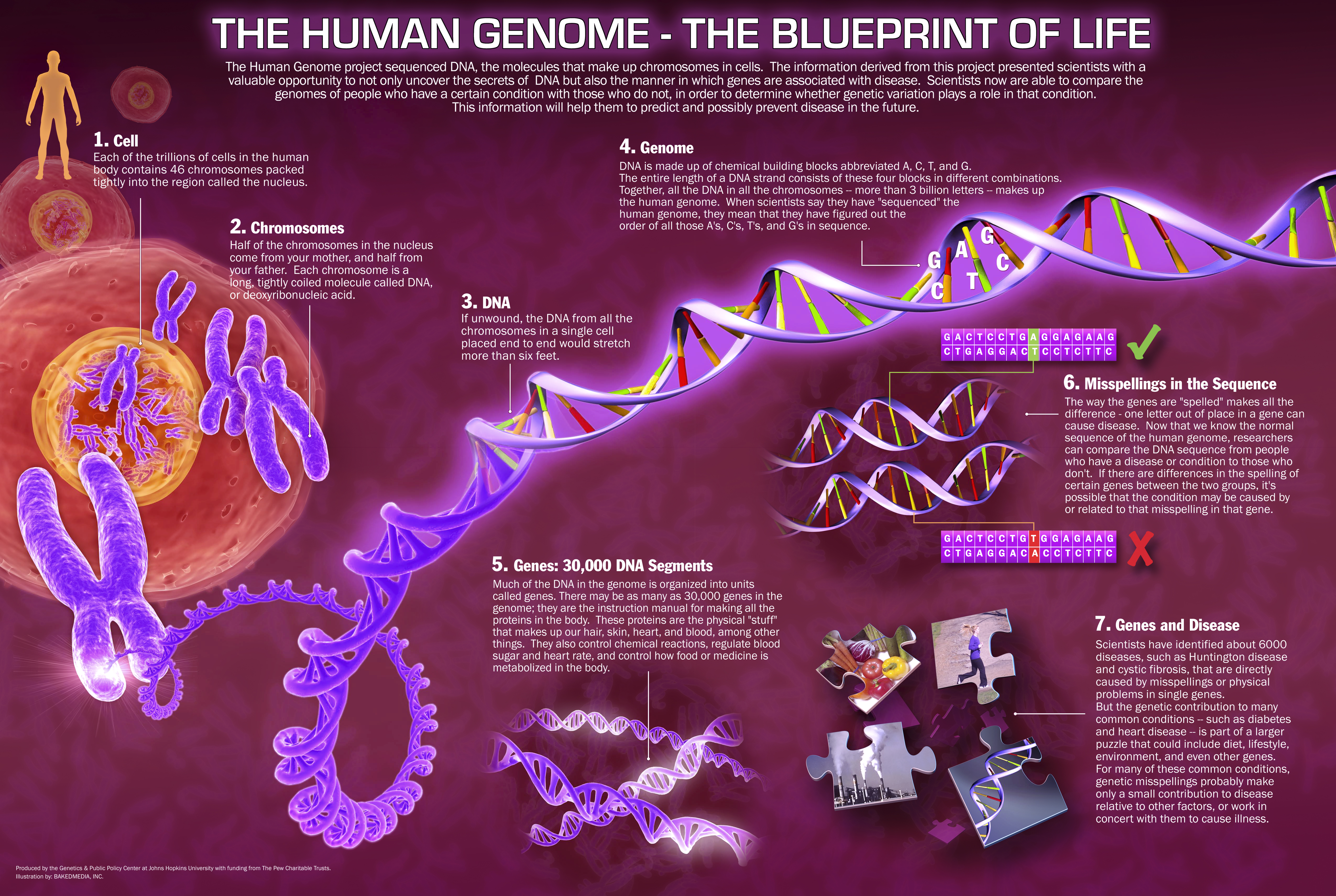
IMAGE: Illustration of the human genome, from the genome to a chromosome, and from a chromosome to genes.
IMAGE: An infographics explaining the Genome
For more clearer image click
http://www.infohow.org/wp-content/uploads/2012/11/The-Human-Genome.jpg
Future hopes for Human Genome Project
An ambitious new initiative, The Cancer Genome Atlas (
http://cancergenome.nih.gov/), aims to identify all the genetic abnormalities seen in 50 major types of cancer. Based on a deeper understanding of disease at
the genomic level, we will see a whole new generation of targeted
interventions, many of which will be drugs that are much more effective
and cause fewer side effects than those available today. Individualized
analysis based on each person’s genome will lead to a powerful form of
preventive, personalized and preemptive medicine. By tailoring
recommendations to each person’s DNA, health care professionals will be
able to work with individuals to focus efforts on the specific
strategies from diet to high-tech medical surveillance that are most
likely to maintain health for that particular individual.
The increasing ability to connect DNA variation
with non-medical conditions, such as intelligence and personality
traits, will challenge society, making the role of ethical, legal and
social implications research more important than ever.
What will genome research mean for pharmacists ???
Pharmacogenomics is a field that looks at how
genetic variation affects an individual’s response to a drug.
Pharmacogenomic tests can already identify whether or not a breast
cancer patient will respond to the drug Herceptin, whether an AIDS
patient should take the drug Abacavir, or what the correct dose of the
blood-thinner Warfarin should be.
IMAGE: How DNA test can reveal effectiveness of drugs and group it into certain classification
The Human Genome Project will provide data to pharmacists and researchers that can lead to the development of better drugs. Rather than screening for chemicals with broad action against a disease, researchers are now using genomic information to design drugs targeted at specific pathways involved in the disease. The hope is that this 'new generation of drugs will work better and cause fewer side effects than current treatment . Such efforts are already starting to pay off, as seen of gene based drugs in the treatment of leukaemia and other cancers. But that's not all. This new. more individualized approach to health care will extend far beyond the drugs you receive


Within the next decade, genetic tests are expected to become available to predict our risk for many common conditions. Such tests will signal the end to the current "one-size-fits-all" approach to health care. Based on the information in your genome, our health provider will develop more personalized strategies for detecting, treating and preventing disease. By learning more about our genome and what it may mean for the future, we have taken a major step towards a new exiting era :
The Genome Era
References
http://report.nih.gov/NIHfactsheets/ViewFactSheet.aspx?csid=45&key=H#H
http://www.genome.gov/10001772#al-1
http://www.infohow.org/wp-content/uploads/2012/11/The-Human-Genome.jpg