Protein structure is actually a polymer, it is a sequence formed from various amino acids or also referred to as residues. It is more specifically known as a polypeptide. In order for the protein to function efficiently, proteins bond via non-covalent interactions such as hydrogen bonds and ionic interactions, hydrophobic packing and Van der Waals forces, to enable them to fold into one or more specific spatial conformations. proteins come in various sites ranging from tens to several thousand residues. They are usually classified by nanoparticles sizes that is 1-100nm. however there are very large aggregates that can form protein subunits as well for example, many thousand of actin molecules form a micro-filament.
A protein undergoes structure changes while performing biological functions these transitions between them that occur are called conformation changes while the different changes of the same protein is referred to as different conformations.
These are four different levels of protein structure. The residual level which is the first and simplest level which composes of amino acids that have a backbone part and uniquely a side chain to each type of residue. Then, comes the primary structure, which is a linear sequence of a polypeptide chain that is held together by covalent bonds such as peptide bonds. these bonds are formed during the biosynthesis process or the translation process. The secondary structure are the alpha helix and beta sheets or strands, which form a super secondary unit when several of them are attached together. The third level of protein structure is the tertiary structure which is also known as the 3D or three dimensional structure which consists of either single, double or triple bond structures. The secondary structure is basically folded into a compact globular structure forming a tertiary structure. Finally, the quaternary structure is the the three dimensional structure and how it fits together.

Figure 1: The differences between primary sequence of protein in bioinformatics data analysis algorithm and the 3D structure produced
Figure 2: 3D Structure of Hemoglobin, one of the most common quarternary protein structure in our body
Figure 2: 3D Structure of Hemoglobin, one of the most common quarternary protein structure in our body
Tertiary
Structure -
refers to the comprehensive 3-D structure of the polypeptide chain of a
protein. There are several types of bonds and forces that hold a protein in its
tertiary structure. Hydrophobic interactions greatly
contribute to the folding and shaping of a protein. The "R" group of
the amino acid is either hydrophobic or hydrophilic. The amino acids with
hydrophilic "R" groups will seek contact with their aqueous
environment, while amino acids with hydrophobic "R" groups will seek
to avoid water and position themselves towards the center of the protein. Hydrogen
bonding in the polypeptide chain and between amino acid "R"
groups helps to stabilize protein structure by holding the protein in the shape
established by the hydrophobic interactions. Due to protein folding, ionic
bonding can occur between the positively and negatively charged
"R" groups that come in close contact with one another. Folding can
also result in covalent bonding between the "R" groups of cysteine
amino acids. This type of bonding forms what is called a disulphide
bridge. Interactions called Van Der Walls forces also assist in the stabilization of protein
structure. These interactions pertain to the attractive and repulsive forces
that occur between molecules that become polarized. These forces contribute to
the bonding that occurs between molecules.
Figure 3: The 3D structure of protein myoglobin
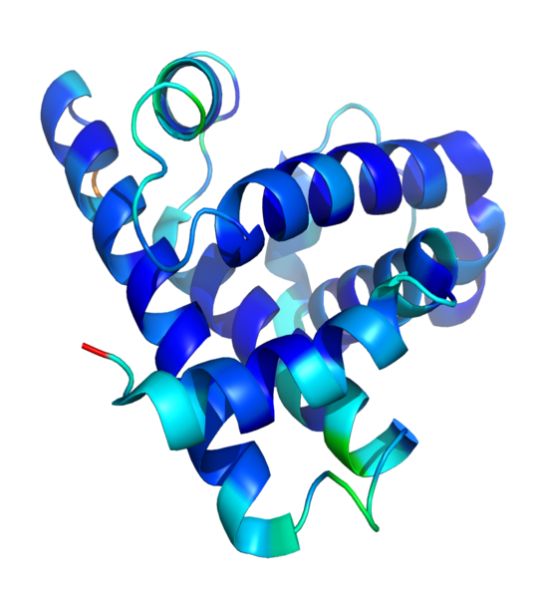
Figure 4 : A representation of the 3D structure of myoglobin showing colored alpha helices. This protein was the first to have its structure solved by X-ray crystallography

Figure 4 : A representation of the 3D structure of myoglobin showing colored alpha helices. This protein was the first to have its structure solved by X-ray crystallography

No comments:
Post a Comment